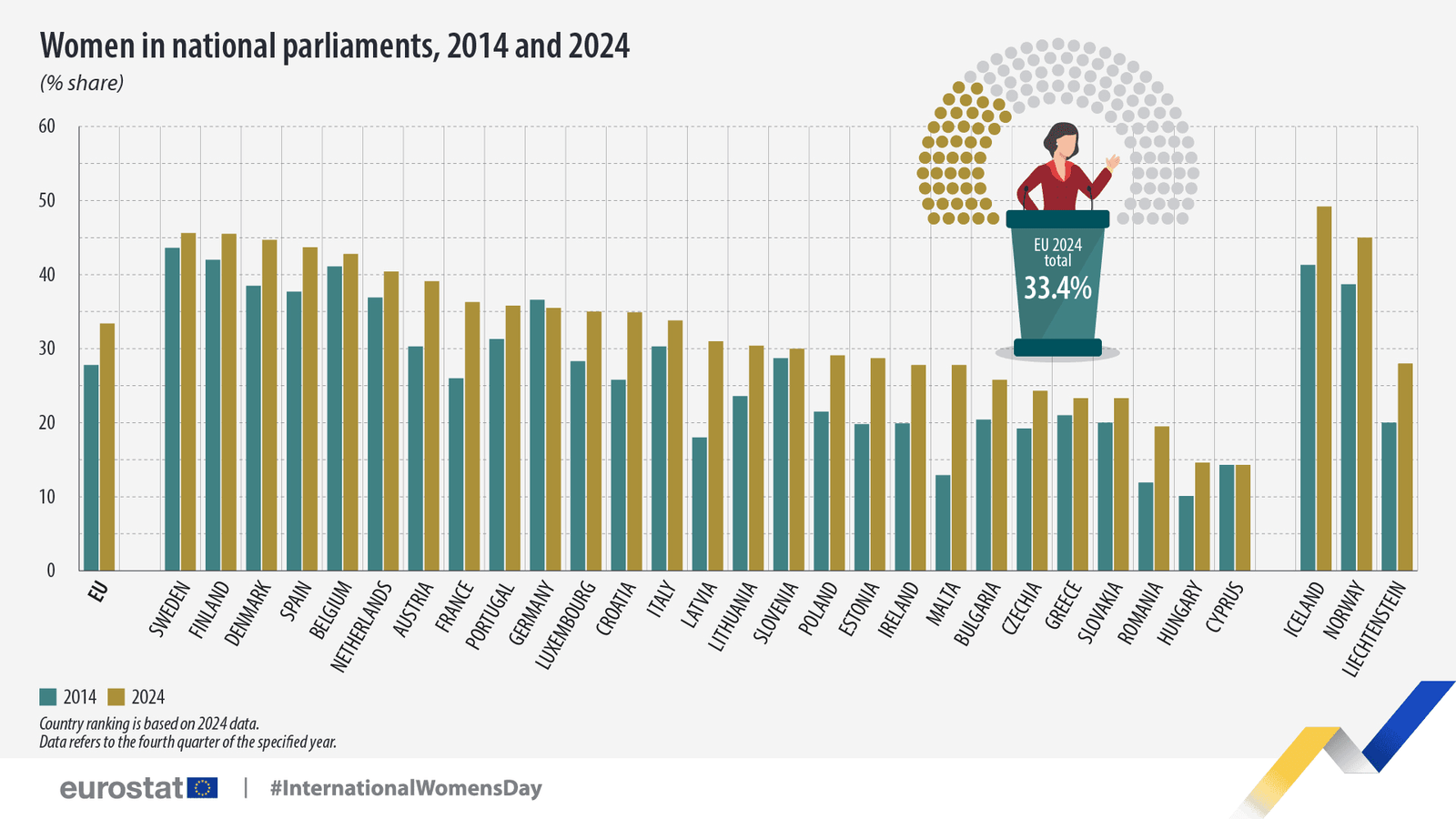
Women now hold a third (33.4%) of parliamentary seats across the European Union, marking a steady rise in political representation over the past decade. Fresh Eurostat data shows this figure reflects a 5.6 percentage point increase compared to 2014. But while some EU nations are closing the gender gap in politics, others remain significantly behind—Cyprus among them.
Cyprus: The Lowest Female Representation In The EU
Cyprus stands at the bottom of the EU ranking for female parliamentary representation, with just 14.3% of MPs being women. This figure has remained unchanged since 2014, highlighting a decade of stagnation in gender equality within the country’s legislature. Compared to the EU average of 33.4% and the frontrunners—Sweden (45.6%), Finland (45.5%), and Denmark (44.7%)—Cyprus lags significantly behind.
Follow THE FUTURE on LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, X and Telegram
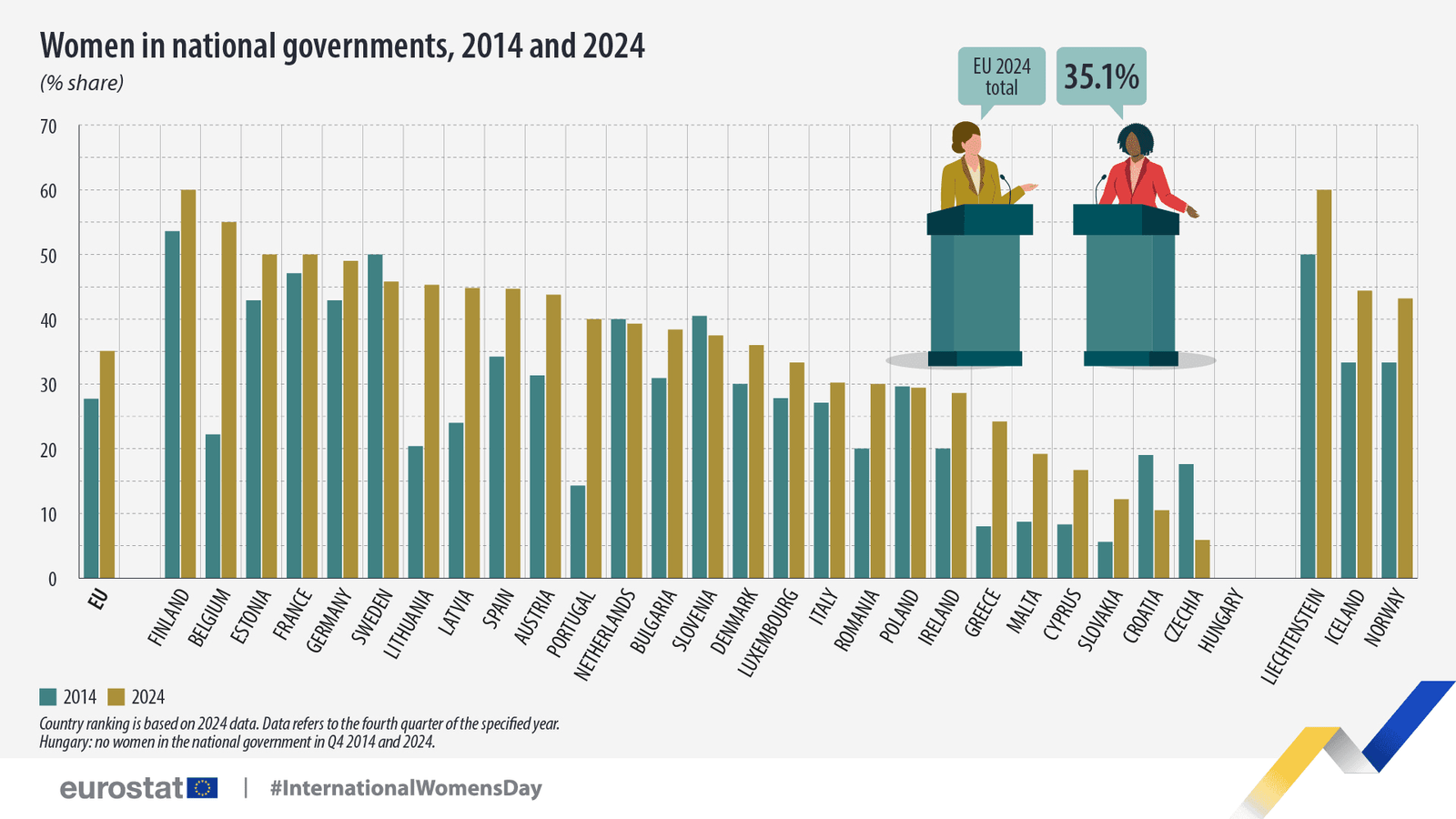
The situation is no better in the national government. Unlike countries making progress in appointing women to ministerial roles, Cyprus remains far from achieving gender balance. While Belgium (55.0%), Estonia (50.0%), and France (50.0%) now have at least half of their national governments made up of women, Cyprus remains among the least progressive in this area.
Uneven Progress Across The EU
Despite Cyprus’s stagnation, other EU countries have made significant strides. Malta (+14.9 pp), Latvia (+13.0 pp), and France (+10.3 pp) have seen the largest increases in female parliamentary representation over the past decade. Similarly, Belgium (+32.8 pp), Portugal (+25.7 pp), and Lithuania (+24.9 pp) recorded the biggest jumps in female participation in national governments.
Meanwhile, some EU nations remain stark outliers. Hungary had no women in its national government in 2024, while Czechia (5.9%) and Croatia (10.5%) had some of the lowest shares of female ministers.
As Europe pushes toward greater gender equality in politics, the gap between progressive and lagging nations continues to grow. The question remains: will countries like Cyprus take action to close the divide, or will they continue to fall behind?
Read Gender Equality Remains A Top Priority, Says Cypriot President







