House prices across Europe are set to continue climbing in 2025, propelled by an ongoing supply-demand imbalance. While most countries will see growth, France stands out as an exception, with prices expected to dip temporarily due to affordability issues and political uncertainties. Fitch Ratings’ housing and mortgage outlook for 2025 predicts that nominal home prices will rise in the low to mid-single digits in most countries over the next two years.
Top European Markets to Watch
- Netherlands: House price growth is projected to slow from the current 13% to 8%-10% in 2025, and 6%-8% in 2026. This still represents one of the fastest growth rates globally, driven by a limited housing supply due to rising material and labour costs. Population growth and shrinking household sizes further fuel demand. Government programmes aimed at supporting first-time buyers could also boost the market, although tighter fiscal policies may temper purchasing power.
- Spain: House prices are expected to increase by 4%-6% in 2025 compared to 2024, with further growth of 5%-7% anticipated in 2026. Falling interest rates and improving consumer confidence are key drivers, while the housing shortage remains acute, with new construction meeting only half the needs of new household formations.
- Germany: Modest growth of 2%-4% is forecast for both 2025 and 2026, up from Fitch’s estimate of 1.5% for 2024. Rising rents are making homeownership increasingly attractive, despite moderate wage growth limiting affordability.
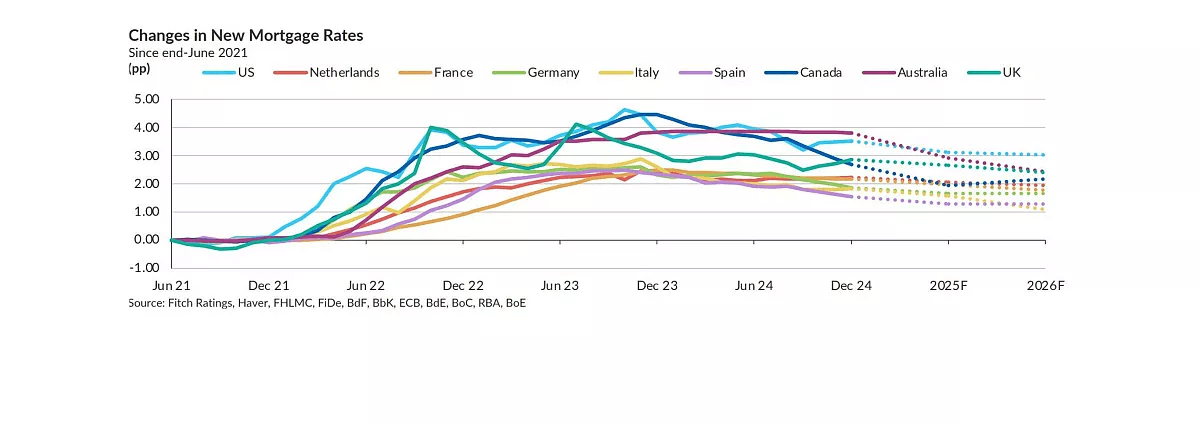
- UK: House prices are predicted to grow by 2%-4% in 2025 and 2026. Declining mortgage rates and strong labour market conditions will support the market, with lenders pricing in policy rates reaching 3.5% in 2025.
- Denmark: Similar to the UK, house prices in Denmark are expected to rise by 2%-4% in 2025 and 2026, driven by lower interest rates and moderate growth in disposable income.
- Italy: Slower growth of 0.5%-2.5% is expected in 2025 and 2026. High mortgage rates are dampening demand, while most transactions involve older properties rather than new builds, contributing to limited price increases.
Key Drivers of Price Growth
- Limited Supply: High land, labour, and material costs, along with regulatory barriers, are restricting new housing developments in most markets.
- Improved Economic Conditions: Low unemployment, real wage growth, and easing inflation are leaving consumers with more disposable income, driving demand.
- Falling Mortgage Rates: Fitch Ratings expects mortgage rates to decline to around 2.5% over the next two years, which will enhance affordability for buyers.
Market Exceptions and Challenges
- France: House prices are expected to decline in 2025 due to strained affordability and political uncertainties. However, the pace of decline will slow compared to 2024, and prices are projected to rebound in 2026 as the market stabilises.
- Climate and Regulatory Concerns: Flood risks and EU regulations promoting sustainable construction practices could influence market dynamics, increasing costs while boosting demand for energy-efficient homes.
Global Perspective and Risks
Globally, the strongest home price growth is forecast in the Netherlands, Canada, Brazil, and Mexico. In these markets, factors such as government programmes for first-time buyers and rising construction costs are key drivers.
Follow THE FUTURE on LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, X and Telegram
Despite the expected growth, Fitch warns that unexpected economic challenges, such as higher-than-expected inflation or weaker household income, could disrupt these trends. Rising property taxes, insurance, and maintenance costs may also deter potential buyers.
Europe’s housing market in 2025 will be shaped by the interplay of supply constraints, economic conditions, and regulatory factors. For buyers, investors, and policymakers, staying attuned to these trends will be crucial in navigating an increasingly competitive landscape.







